As organizations increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, HR departments are under pressure to deliver accurate, timely, and trustworthy analytics. Whether it’s for workforce planning, diversity initiatives, or employee retention strategies, HR analytics is only as good as the data it is built on. But how can HR professionals ensure the insights they provide are credible and traceable? The answer lies in data lineage—a foundational concept that ensures transparency, accountability, and confidence in HR analytics.
Understanding Data Lineage in HR –
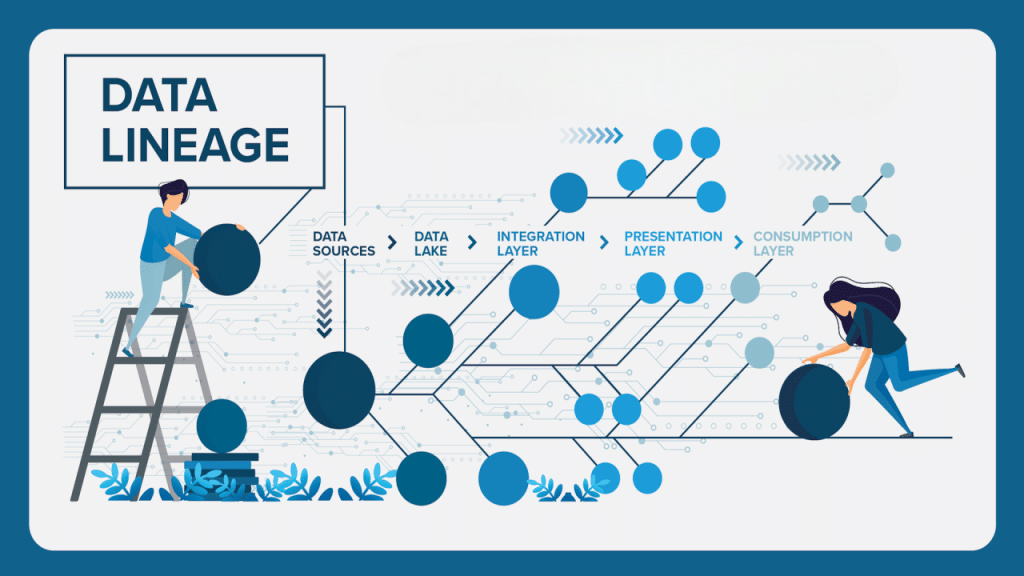
Data lineage refers to the ability to track and visualize the lifecycle of data as it moves through systems—from its original source to the final report or dashboard. In the HR context, this means tracing metrics like headcount, turnover rates, or employee engagement scores back to their raw source data, such as HRIS (Human Resource Information System), payroll platforms, or survey tools. Data lineage offers a transparent view of how data is transformed, aggregated, and reported, helping HR teams understand not just what an insight is, but how it was derived.
The Growing Importance of Data Lineage in HR –
As HR teams embrace analytics platforms and integrate multiple systems, the complexity of data flows has increased significantly. Employee data often passes through various transformations, filters, and calculations before it reaches executive dashboards. Without a clear view of these steps, it becomes difficult to validate the accuracy of insights or debug issues when discrepancies arise. Data lineage solves this by mapping each step in the data journey, offering both technical and business users a comprehensive understanding of data processes.
Ensuring Data Trust and Compliance –
Trust in HR analytics is paramount. If an executive questions the accuracy of a workforce cost projection or diversity dashboard, the HR analyst must be able to explain where the data came from, what transformations it underwent, and who had access to it. Data lineage supports this accountability by providing a clear audit trail. Moreover, with increasing data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, understanding the origins and flow of personal employee data is critical for compliance. Data lineage helps ensure that sensitive data is used appropriately and that access is limited to authorized users.
Driving Better Decision-Making –
Accurate decision-making relies on the credibility of the underlying data. If an organization is considering a restructuring initiative based on attrition patterns or skills gaps, stakeholders must trust that the insights are derived from complete and accurate data. Data lineage enables HR teams to validate the integrity of the data, ensuring that the decisions being made are based on a strong foundation. When leadership knows the path from raw data to dashboard is clearly documented, they are more likely to act with confidence on HR recommendations.
Improving Data Quality and Governance –
One of the indirect but powerful benefits of implementing data lineage is the improvement in overall data quality. By visualizing the data journey, HR teams can identify redundancies, inconsistencies, or manual touchpoints that introduce errors. This allows for proactive governance and better data stewardship. For example, if a turnover report is consistently producing different results than expected, data lineage can help pinpoint whether the issue lies in the source data, a transformation rule, or a faulty filter in the analytics layer.
Key Tools and Technologies for HR Data Lineage –
Modern HR analytics platforms increasingly offer built-in data lineage capabilities. Tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Looker provide visual mapping of data sources and transformations. For more advanced environments, data catalog tools such as Collibra, Alation, or Microsoft Purview can integrate with HR data warehouses and pipelines to provide automated lineage tracking. Integration with ETL platforms like Talend, Informatica, or Apache Airflow also helps maintain a clear picture of how HR data is processed and consumed.
Challenges in Implementing Data Lineage in HR –
Despite its benefits, establishing data lineage in HR is not without challenges. HR systems often contain sensitive and siloed data, making integration complex. Additionally, not all HR professionals are trained in data engineering or lineage tracking. Overcoming these barriers requires collaboration between HR, IT, and data governance teams. Organizations must also invest in user-friendly tools and provide training to help HR staff interpret lineage maps and metadata effectively.
Conclusion –
In the evolving landscape of HR analytics, transparency and trust are non-negotiable. Data lineage provides the visibility and accountability needed to ensure that HR insights are not only powerful but also provable. By tracing insights back to their data origins, organizations can enhance the quality of their decision-making, stay compliant with regulations, and build stronger trust with stakeholders. As data continues to shape the future of HR, data lineage will become a critical pillar in any forward-looking analytics strategy.